India’s independence in 1947 was not just the result of political struggle—it was the beginning of a new journey to define the nation’s identity, values, and governance. The Constitution of India, adopted on 26 January 1950, became the cornerstone of our democracy. While we often remember freedom fighters for their role in ending British rule, many also made significant contributions to framing the Constitution.
In this article, we highlight key freedom fighters who shaped India’s Constitution, their ideals, and the principles they brought into our foundational legal document.
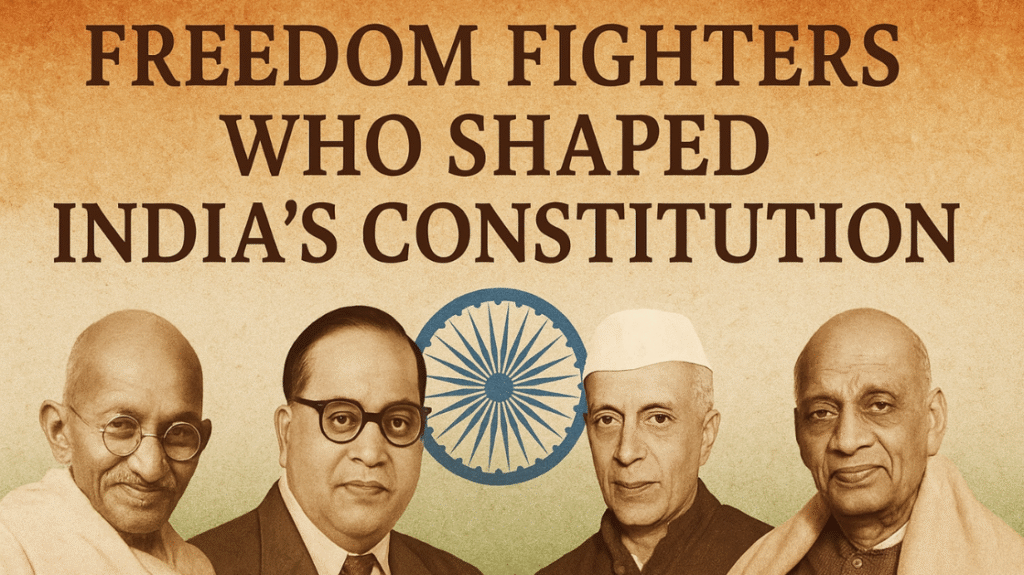
Key Freedom Fighters Who Shaped India’s Constitution
1. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar – The Chief Architect
- Role in Freedom Movement: Advocate for social justice, equality, and rights for the marginalized.
- Contribution to the Constitution:
- Chairman of the Drafting Committee.
- Introduced provisions for Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy.
- Ensured equality before law, abolition of untouchability, and protection of civil liberties.
- Legacy in the Constitution: Ambedkar’s vision ensured the Constitution safeguarded against discrimination and promoted social justice.
2. Mahatma Gandhi – The Soul of India
- Role in Freedom Movement: Leader of non-violent resistance and mass movements like Dandi March & Quit India Movement.
- Influence on the Constitution:
- Although not directly part of the drafting, Gandhi’s ideals of non-violence, decentralization, and self-reliance influenced constitutional provisions like Panchayati Raj and Fundamental Duties.
- Legacy: The emphasis on morality, truth, and harmony still guides the Indian legal and political framework.
3. Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru – Visionary of Modern India
- Role in Freedom Movement: Prominent leader in Congress, advocate of modern education, science, and democracy.
- Contribution to the Constitution:
- Presented the Objectives Resolution in 1946, which became the Preamble of the Constitution.
- Championed secularism, socialism, and democratic governance.
- Legacy: His vision laid the foundation for India’s parliamentary system and foreign policy principles.
4. Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel – The Iron Man of India
- Role in Freedom Movement: Played a crucial role in uniting India post-independence.
- Contribution to the Constitution:
- Ensured integration of princely states into the Indian Union.
- Advocated for a strong central government to maintain unity.
- Legacy: His efforts in building administrative and political unity are reflected in the Constitution’s federal structure.
5. Rajendra Prasad – First President of India
- Role in Freedom Movement: A devoted Gandhian, leader in Bihar movements, and Congress president during critical times.
- Contribution to the Constitution:
- Served as the President of the Constituent Assembly.
- Ensured debates remained democratic and consensus-driven.
- Legacy: His leadership style promoted harmony in decision-making.
6. Alladi Krishnaswami Ayyar – Legal Luminary
- Role in Freedom Movement: A staunch supporter of constitutional reforms and legal modernisation.
- Contribution to the Constitution:
- Expert in constitutional law; contributed significantly to drafting legal clauses.
- Advocated for judicial independence and fundamental rights.
- Legacy: Helped shape India’s judiciary as a strong, independent pillar.
7. B.N. Rau – Constitutional Advisor
- Role in Freedom Movement: Administrative expert, worked in legislative reforms before independence.
- Contribution to the Constitution:
- Prepared the initial draft, later revised by the Drafting Committee.
- Researched and incorporated best practices from global constitutions.
- Legacy: His groundwork ensured the Constitution was legally sound and globally inspired.
Conclusion
India’s Constitution is not merely a legal text—it is the culmination of the dreams, sacrifices, and intellect of our freedom fighters. Their contributions ensured that India emerged as a sovereign, democratic, and inclusive nation.
As we celebrate Independence Day and reflect on our democratic journey, remembering these leaders reminds us of the responsibility we hold to uphold the Constitution in spirit and practice.
To read more Indian Laws and news, visit Legal Guide India